What is Nuclear Fission?
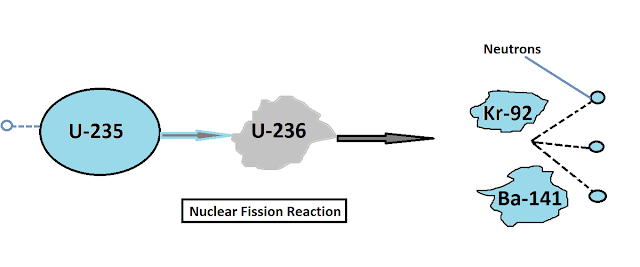
- The reaction in which a heavy nucleus splits into two or more smaller nuclei with the evolution of a large amount of energy is called nuclear fission reaction.
- The fission process often produces gamma photons, and release a very large amount of energy.
- Nuclear fission of heavy elements was discovered on December 17, 1938, by German Otto Hahn.
- Fission is a form of nuclear transmutation because the resulting fragments are not the same element as the original atom.
-Many types of nuclear reactions are currently known but Nuclear fission differs importantly from other types of nuclear reactions, in that it can be amplified and sometimes controlled via a nuclear chain reaction (one type of general chain reaction). In such a reaction, free neutrons released by each fission event can trigger yet more events, which in turn release more neutrons and cause more fission.
Nuclear Power Plant-
The most important use of nuclear energy is the generation of electricity. This is done by using the setup, called the nuclear power plant.
- Electricity was generated by a nuclear reactor for the first time ever on September 3, 1948, at the X-10 Graphite Reactor in Oak Ridge, Tennessee, the US which was the first nuclear power station to power a light bulb. The second, larger experiment occurred on December 20, 1951, at the EBR-I experimental station near Arco, Idaho.
- On June 27, 1954, the world's first nuclear power station to generate electricity for the power grid, the Obninsk Nuclear Power Plant, started operations in Obninsk of the Soviet Union. The world's first full-scale power station, Calder Hall in England, opened on October 17, 1956. The world's first full-scale power station solely devoted to electricity production—Calder Hall was also meant to produce plutonium—the Shippingport Atomic Power Station in Pennsylvania, the United States was connected to the grid on December 18, 1957.
Principle of Nuclear Power Plant
It is a thermal power station in which heat source is a nuclear reactor. The heat produced in a controlled nuclear fission reaction is utilised for producing steam. The steam is used to run the turbine connected to generator electricity is generated.
Components of a Nuclear Power Plant
1.Nuclear Reactor- It is an arrangement in which controlled nuclear fission takes place.
There are several components of a nuclear reactor which are as follows:
Ⅰ.Fissionable Fuel- Uranium-235 and Uranium-239 are used.U-235 is fissile which means that it is easily split and gives off a lot of energy making it ideal for nuclear energy.
Ⅱ. Moderator- Moderator decreases the energy of neutrons so that they can be further used for fission reaction. Heavy water(D2O) and graphite are used as a moderator.
Ⅲ. Control Rod- Rods of Cadmium or Boron is used to absorb the excess neutrons produced in fission of uranium nucleus so that the chain reaction continues to be controlled.
Ⅳ. Coolant- A large amount of heat is produced during fission. The coolant absorbs the heat and prevents a rise in the temperature. The coolant may be water, Heavy-water or gas like helium or Carbon dioxide.
2. Heat Exchanger- The reactor is connected to a heat exchanger. Here, the heat produced in the reactor is transferred to the water by circulating a coolant through a coiled pipe. The water gets converted into steam. The coolant is pumped back to the reactor.
3. Steam Turbine- The steam generated in the heat exchanger is used to run the steam turbine. The spent steam is sent back as hot water to the heat exchanger.
4. Electric Generator- The shaft of the steam turbine is connected to an electric generator(or Dynamo) and electricity so produced is sent for transmission.




Comments
Post a Comment